Conventional medicine treats dyslipidemia
as the major source of atherosclerosis, and promotes statin drugs and avoidance of
dietary animal fats as the best way to prevent atherosclerosis.
However, Dr. Starr argues against animal fats as a source of atherosclerosis:
... during and after World War II, the vast majority of people in Europe were deprived of eggs
and animal fats. Yet, thousands of autopsy results from this period reveal that the rate of
atherosclerosis was accelerated to four times the rate before or after this period
[Starr2005, pg 166].
Dr. Starr continues by pointing out the "French Paradox" - the French diet is high
in saturated fats such as eggs and butter, but they suffer lower rates of heart attacks.
Dr. Weyrich notes that this has sometimes been attributed to the consumption of red wine,
but also points out that at least one study shows that a 60% fat diet is more effective
in improving dyslipidemia and losing weight than a 30% fat diet.
As summarized by Dr. Starr, the results of the study reported by Duke University in 2002
are as follows [need reference]:
| % Fat in diet | Weight loss # | % Change HDL | % Change TG |
|---|
| 60% | 30 # | up 11% | down 49% |
| 30% | 20 # | no change | down 22% |
In conclusion, while dyslipidemia may be associated with atherosclerosis, association
does not imply causality. In fact, avoidance of dietary fats is counterproductive to correcting
dyslipidemia or preventing atherosclerosis.
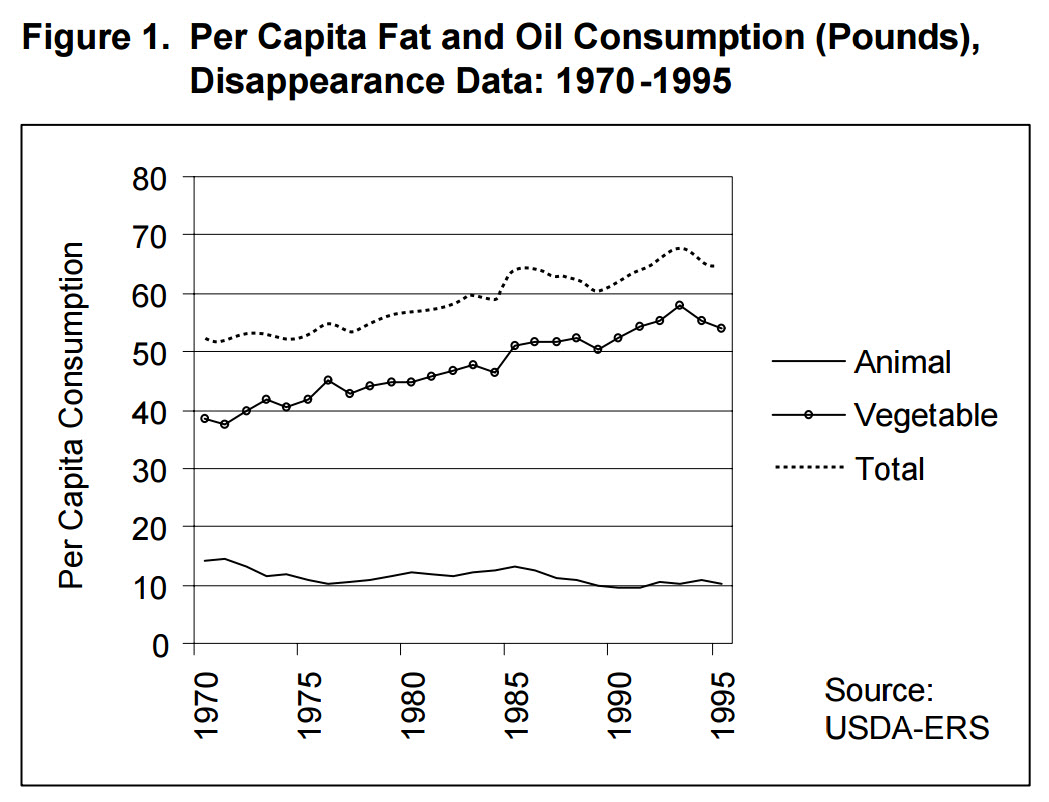
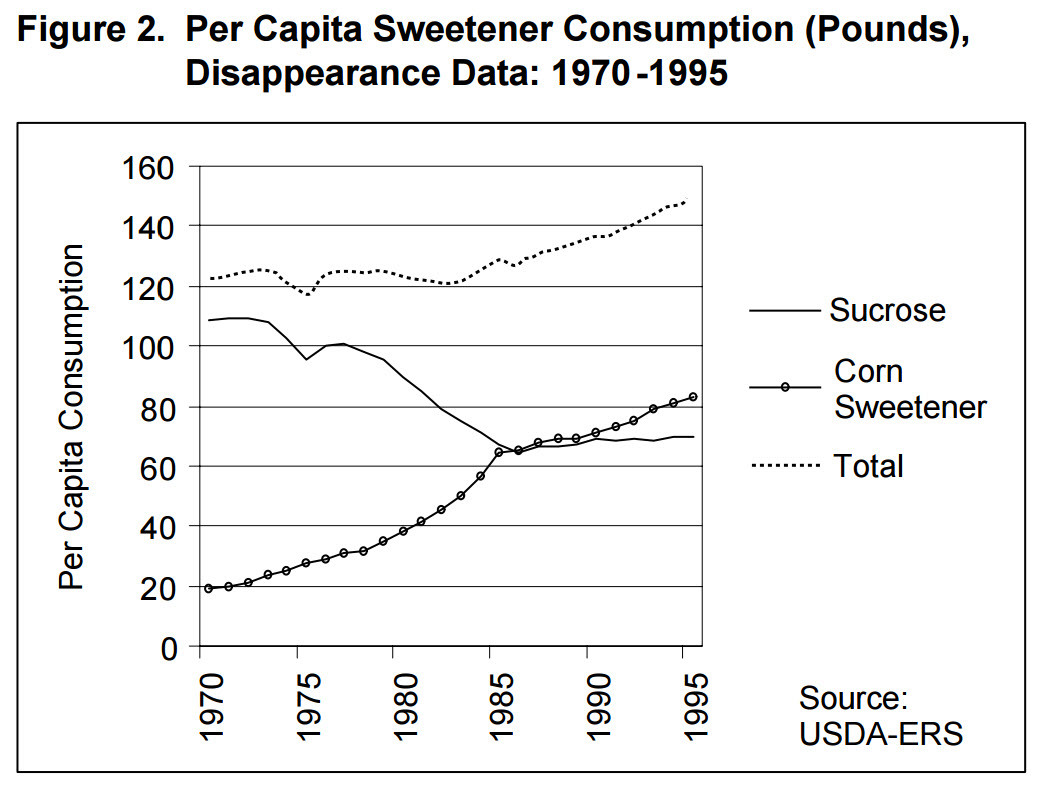
This is obvious by consideration of the historical graphs (Figures 1 and 2 below)
[King2000] show that the well-known rise of heart disease in
the United States over the past 50 years parallels the rise in the consumption of high-fructose corn syrup and other sweeteners (Figure 2), and the rise in the consumption
of vegetable oils (Figure 1). This historical data do not support the theory that consumption of animal fat including eggs is linked to heart disease.
On the other hand, correcting hypothyroidism appears to benefit
both dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis - suggesting that hypothyroidism may be a causative
factor in both dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis.


